is regulation of blood glucose positive feedback Glucose homeostasis sugar levels diabetes body human feedback negative insulin insipidus biology maintain symptoms treatment after general url reference ch45
Diabetes insipidus is a health condition that is often quite misunderstood. Despite the similarity in name to diabetes mellitus, the two conditions are not related. Diabetes insipidus is a condition that results when your body is unable to produce enough ADH (anti-diuretic hormone) or when your kidneys fail to respond appropriately to ADH. The symptoms of diabetes insipidus can be quite distressing, and can include excessive thirst and urination, as well as dehydration. In severe cases, the condition can even lead to seizures or coma. Fortunately, with proper diagnosis and treatment, most people with diabetes insipidus are able to manage their symptoms and lead normal, healthy lives. One of the most effective treatments for diabetes insipidus is the use of desmopressin, a synthetic version of ADH. Desmopressin is usually administered via nasal spray or oral tablet, and can help to reduce the amount of urine that your body produces. Other treatments may include medications to reduce the amount of urine produced or surgery to correct any underlying issues. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of diabetes insipidus, it is important to seek medical attention as soon as possible. Your doctor can help to diagnose the condition and recommend an appropriate course of treatment. In the meantime, there are a few things that you can do to manage your symptoms. It is important to stay hydrated, both by drinking plenty of water and by avoiding substances that can dehydrate you. Additionally, you may want to consider reducing your salt intake, as excess salt can exacerbate dehydration. With proper treatment and self-care, most people with diabetes insipidus are able to manage their symptoms and enjoy a full, healthy life. If you have any concerns about the condition, speak to your doctor or a qualified healthcare provider. They can help you to understand the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for this condition, and work with you to create a treatment plan that suits your individual needs.
If you are looking for #113 The control of blood glucose | Biology Notes for A level you’ve came to the right page. We have 5 Pictures about #113 The control of blood glucose | Biology Notes for A level like Feedback loops | Biology Quiz - Quizizz, #113 The control of blood glucose | Biology Notes for A level and also diabetes insipidus symptoms and treatment Jackson MS. Read more:
#113 The Control Of Blood Glucose | Biology Notes For A Level
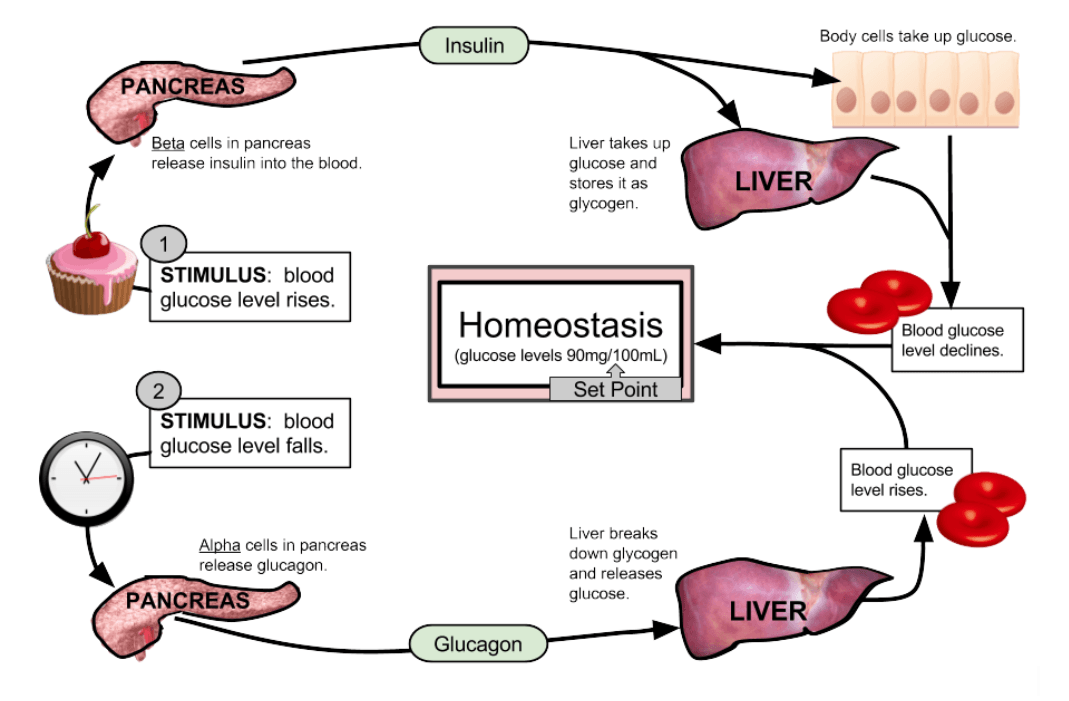
 biology4alevel.blogspot.comblood glucose control summary homeostasis level cycle sugar liver concentration does low insulin fuel loop break feedback physiology regulate eating
biology4alevel.blogspot.comblood glucose control summary homeostasis level cycle sugar liver concentration does low insulin fuel loop break feedback physiology regulate eating
Pin On Biology
 www.pinterest.esglucose glucagon feedback blood insulin sugar loops regulation hormones system pancreatic endocrine diabetes diabetic worksheet nursing answers anatomy biology pathophysiology
www.pinterest.esglucose glucagon feedback blood insulin sugar loops regulation hormones system pancreatic endocrine diabetes diabetic worksheet nursing answers anatomy biology pathophysiology
Diabetes Insipidus Symptoms And Treatment Jackson MS
iiocbnoi.blogspot.comglucose homeostasis sugar levels diabetes body human feedback negative insulin insipidus biology maintain symptoms treatment after general url reference ch45
Feedback Loops | Biology Quiz - Quizizz
Hormones · Anatomy And Physiology
 philschatz.comfeedback hormones negative loop endocrine physiology system control stress pathways hormone glucocorticoid regulation release anatomy gland adrenal hypothalamus glucocorticoids loops
philschatz.comfeedback hormones negative loop endocrine physiology system control stress pathways hormone glucocorticoid regulation release anatomy gland adrenal hypothalamus glucocorticoids loops
Feedback glucose loops negative glucagon biology blood homeostasis sugar positive explain loop insulin levels role pancreas high libretexts between after. Blood glucose control summary homeostasis level cycle sugar liver concentration does low insulin fuel loop break feedback physiology regulate eating. Feedback hormones negative loop endocrine physiology system control stress pathways hormone glucocorticoid regulation release anatomy gland adrenal hypothalamus glucocorticoids loops